Agile Family of Flexible Project Management Methodologies
READ WHOLE ARTICLE
If it is expected to accomplish an objective — on time and within budget, obviously – knowledge of management is a must-know. Whether up to the development of a new software, a promoting campaign, or the landing of a human on Mars, project management makes it conceivable to succeed.
All projects are different. There is no perfect project management system suitable for each type of Agile project management methodologies. Also, there is no system that would suit every manager and was convenient for all team members. However, during the existence of project management, many effective approaches, methodologies and standards were created, which can be adopted. We will make the overview of the most popular of them today.
The approaches developed are very different from each other. They differ in application, detail, self-sufficiency and formalization. The purpose of this article is to provide the broadest overview of the approaches in project management. Here we will look at Agile and its helpers: Scrum and Kanban management methodologies.
How to Prepare for the Brief with Your Software Development Team
Agile
So, what is agile methodology in project management? Agile is a family of “flexible” approaches to software development. Such approaches are also sometimes called agile frameworks or agile methodologies.
Agile emerged in the IT environment, but then spread to other areas – from industrial engineering to artificial intelligence.
Agile assumes that the project does not need to rely only on previously created detailed plans. It is crucial to concentrate on the constantly changing conditions of the external and internal environment and to take into account feedback from customers and users. This encourages developers and engineers to experiment and find new solutions, not limiting yourself to rigid frameworks and standards.
The very advantage of Agile is its flexibility and adaptability. It can adapt to almost any conditions and processes of the organization. That is what determines its current popularity and how many systems for different areas were created on its basis.
One of the concepts of Agile: “Response for change is more relevant than following a scheme.” It is the quick and relatively painless reaction to change that causes many large companies to make their processes more flexible. In addition, Agile is great for projects with an “open end”, e.g. launching a service or blog.
Agile is a set of concepts and duties. The weak side is that every team will ought to independently establish its own management system, led by the principles of Agile. This is a complicated and time-consuming process that will need changes throughout the organization, starting with procedures and ending with basic values. This is a thorny path and not all organizations can do it.
Individual agile approaches include scrum and kanban.
Scrum
Scrum is an approach with exact structure. A universal group of pros caries each project life cycle, which is joined by two additional people: the product proprietor and the scrum-ace. The first units the team with the client and scans the development of the project; this is a kind of a mentor. The second encourages the first to compose a business procedure: organizes general meetings, deals with domestic issues, motivates the team and scans compliance with the scrum methodology.
The scrum approach partitions the work procedure into equal sprints – ordinarily these are periods from seven days to a month, contingent upon the project and team. Before it, assignments for this sprint are set and detailed, at the end – the outcomes are talked about, and the team begins a new sprint. Sprints are advantageous to contrast and one another, which enables you to get more work efficiency.
The main scheme of Scrum forms rotates around 5 fundamental meetings: ordering the backlog, planning, daily flyers, summarizing and retrospectives.
1. Backlog Meeting. It is held on the first day of each Sprint. It checks what has already been performed on the project as a whole, what stays to be done and a choice is made about what to do next. The product owner figures out which tasks at this stage are of the most astounding need. This procedure determines the success of the Sprint. All things considered, it relies upon him what esteem the client will get in the sprint.
2. Planning: After the product proprietor has set the priorities, the group will together choose what precisely they will perform and emphasize, how to reach the goal, held at the previous gathering. Groups may utilize distinctive arranging and assessment tools at this stage, as long as they don’t repudiate the standards and rationale of Scrum. Sprint planning is carried out at the very beginning of the iteration, after the Product Ordering Meeting. | 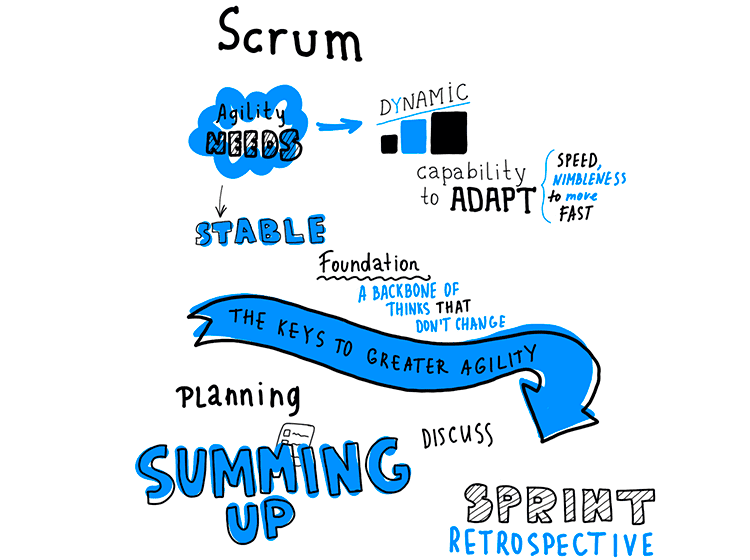 |
3. Daily flyers: Team “players” spend 20 minutes to discuss the tasks and project status. There is no talk about issues or decision making – if after a meeting there are questions and clashes, the Scrum Master and the members involved discuss them on their own. The fly is necessary to exchange information and keep all team members motivated.
4. Summing up: The aim of the step is to analyze and adjust the item being done. The group introduces the work results to all interested parties. The very idea is to ensure that done things meet the client’s desires and is reliable with the targets of the item.
5. Sprint Retrospective: Held following summing up the sprint and before arranging the following sprint. On it, the group discovers how well and easily passed the way toward executing the stage. Examination of exposed issues in work, strategy and cooperation. This stage enables the team to direct a reflection and to hold the next Sprint more effectively.
The weak side is that Scrum was designed for projects that require “quick success” joined with resistance for change. What’s more, this system is appropriate for circumstances where not all colleagues have sufficient experience in the field in which the project is being implemented – consistent correspondence between colleagues considers an absence of experience or capabilities of certain workers because of data and help from associates.
Kanban
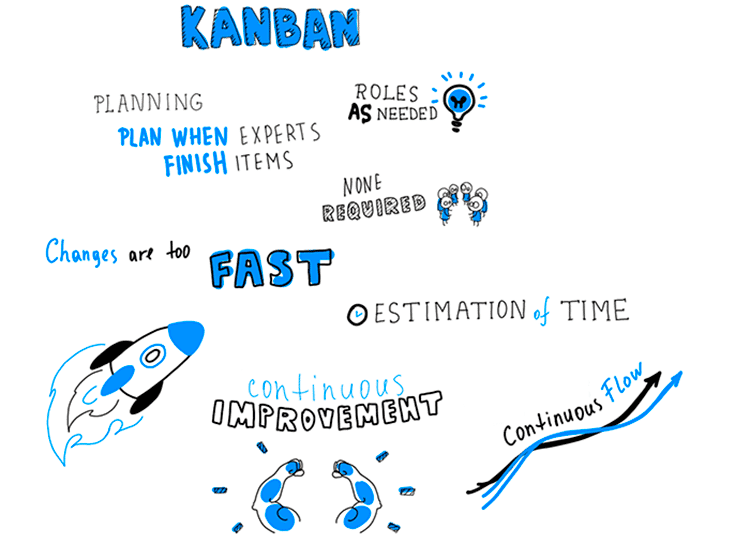
Kanban is explained as a balanced approach. Its task is to balance the work of various specialists within the team and omit a situation where designers are busy for days and developers are bored because of the lack of new tasks.
The main performance indicator in kanban is the average time for the task to complete on the board. The task passed quickly – the team worked productively and harmoniously. The task was delayed – it is necessary to think
At what stage and why did the delays arise and whose work should be optimized.
Your own Kanban framework can be as adaptable as you want it to be – all things considered, from various perspectives Kanban is a perception of the possibility of Agile.
Be that as it may, Kanban has 4 columns that hold the entire framework:
 |
|
- Continuous Improvement: The idea of nonstop improvement showed up in Japan toward the finish of the twentieth century. Its pith is the steady examination of the creation procedure and the scan for approaches to build profitability.
- Like Scrum, Kanban is well suited for a genuinely cohesive team with great correspondence. But, in contrast to Scrum, Kanban has no reasonable due dates set, which is appropriate for inspired and experienced groups.
With appropriate arrangement and management, Kanban can be of extraordinary advantage to the venture group. Precise estimation of the heap in the group, Appropriate arrangement of confinements and focus on consistent improvement – this permits Kanban to spare assets and put on deadlines and financial plan. And all this combined with flexibility.
You can regularly hear that by Kanban, in contrast to Scrum, you can work with practically any group. But, it isn’t so.
The main Kanban weakness is that it is most appropriate for groups whose individuals’ abilities cover with one another. Consequently, they can enable each other to defeat troubles in tackling issues. Without this, Kanban won’t be as compelling as it could be. Additionally, Kanban is more qualified in situations where there are no hard deadlines.
For tight deadlines, Agile Scrum project management methodology is better suited.
Definition of Customer Support: What KPIs You Should Be Tracking for Success?
Final words
IT companies should be really careful and responsible with using such techniques and taking account of all its pros and cons. Each project needs its approach to work with and succeed. Multi-Programming Solutions deals with Agile, Scrum and Kanban professionally and chooses an appropriate way to manage the teamwork for getting maximum benefits from using agile methodology. We know how to create the product which will meet your needs according to the set deadline and budget.
Contact us to start your project!

36 Kings Road
CM1 4HP Chelmsford
England


